I needed to create a .iso file to make a Windows icon. You need to use icotool which is part of icoutils.
apt-get install icoutils
Then:
icotool -c -o launcher_icon_128.ico launcher_icon_128.png
Job done.
I needed to create a .iso file to make a Windows icon. You need to use icotool which is part of icoutils.
apt-get install icoutils
Then:
icotool -c -o launcher_icon_128.ico launcher_icon_128.png
Job done.
ng2icns is a great little tool for creating Mac icons on Linux. It comes in the the incsutils package:
sudo apt-get install icnsutils
To make the installer launch your application after it has been installed you need to add an “Execute launcher” action to your “Finish screen”.
You will need to select which launcher for the installer to run.
I am just making an installer for Windows, Mac and Linux using install4j. However, it isn’t clear from the docs how to change the banner image on the left hand side.
To set it on the Welcome screen, you need to go to Installer -> Welcome and select the “Images For Banner” property,
To change it on the Finish screen, you need to go to installer -> Finish and select the “Image for Banner” property.
Our Bacula server has started failing when backing up its own database. This is a standard job called BackupCatalog. It showed an error like so:
27-Feb 23:29 bacula-dir JobId 6545: shell command: run BeforeJob "/etc/bacula/scripts/<a href="http://make_catalog_backup.pl" target="_blank">make_<wbr />catalog_backup.pl</a> MyCatalog" 27-Feb 23:35 bacula-dir JobId 6545: BeforeJob: mysqldump: Error 2013: Lost connection to MySQL server during query when dumping table `File` at row: 2164125 27-Feb 23:35 bacula-dir JobId 6545: BeforeJob: mysqldump: Couldn't execute 'show table status like 'FileSet'': MySQL server has gone away (2006) ....
Reading the error, it would appear to be a mysqldump problem, rather than a Bacula configuration problem. The mysqldump process was running out of resources. This was because the mysql server wasn’t configured correctly and the server didn’t have enough memory or cpu. I run Bacula on a virtual server and it was therefore quite easy to give an extra two gigs of memory and some more CPU time.
However, to fix the mysql server configuration, I adjusted the following settings in MySQL. I did this by creating a file in the /etc/mysql/conf.d/ directory called bacula.cnf with the following settings and then restarted the server.
[mysqld] wait_timeout = 86400 max_allowed_packet=32M innodb_buffer_pool_size=1G sudo service mysql restart
Install mysqltuner
You might have different mysql configuration issues and therefore have different configurations to change. I would highly recommend mysqltuner to help you diagnose problem. It is designed to analysis your MySQL server and recommend options which could be changed based on your server usages.
Note: Your server needs to be running for over 24 hours before it’s recommendations are useful. So, if you have just restarted the server, it probably won’t be very useful.
apt-get install mysqltuner
Then run:
mysqltuner
And you get a lovely report like so. Note: The reports shown below is for server that has only been up for 15 minutes and the recommendations can’t really be trusted.
>> MySQLTuner 1.0.1 - Major Hayden <major@mhtx.net>
>> Bug reports, feature requests, and downloads at http://mysqltuner.com/
>> Run with '--help' for additional options and output filtering
-------- General Statistics --------------------------------------------------
[--] Skipped version check for MySQLTuner script
[OK] Currently running supported MySQL version 5.5.35-0ubuntu0.12.04.2
[OK] Operating on 64-bit architecture
-------- Storage Engine Statistics -------------------------------------------
[--] Status: -Archive -BDB -Federated +InnoDB -ISAM -NDBCluster
[--] Data in InnoDB tables: 413M (Tables: 25)
[--] Data in PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA tables: 0B (Tables: 17)
[!!] Total fragmented tables: 25
-------- Performance Metrics -------------------------------------------------
[--] Up for: 15m 36s (24K q [26.087 qps], 56 conn, TX: 353K, RX: 4M)
[--] Reads / Writes: 0% / 100%
[--] Total buffers: 192.0M global + 2.7M per thread (151 max threads)
[OK] Maximum possible memory usage: 597.8M (10% of installed RAM)
[OK] Slow queries: 0% (0/24K)
[OK] Highest usage of available connections: 1% (3/151)
[OK] Key buffer size / total MyISAM indexes: 16.0M/98.0K
[!!] Key buffer hit rate: 80.0% (5 cached / 1 reads)
[!!] Query cache efficiency: 17.0% (29 cached / 171 selects)
[OK] Query cache prunes per day: 0
[OK] Sorts requiring temporary tables: 0% (0 temp sorts / 3 sorts)
[OK] Temporary tables created on disk: 19% (54 on disk / 275 total)
[OK] Thread cache hit rate: 94% (3 created / 56 connections)
[OK] Table cache hit rate: 24% (66 open / 273 opened)
[OK] Open file limit used: 4% (48/1K)
[OK] Table locks acquired immediately: 100% (24K immediate / 24K locks)
[!!] InnoDB data size / buffer pool: 413.7M/128.0M
-------- Recommendations -----------------------------------------------------
General recommendations:
Run OPTIMIZE TABLE to defragment tables for better performance
MySQL started within last 24 hours - recommendations may be inaccurate
Enable the slow query log to troubleshoot bad queries
Variables to adjust:
query_cache_limit (> 1M, or use smaller result sets)
innodb_buffer_pool_size (>= 413M)
Top
I recommend using Top to diagnose the load problems on your server. For me, it was clear from the basic numbers that the server was using alot of swap and lots of cpu.
SAR
Finally, I recommend used the excellent sysstat / sar tools to see the history of the CPU and the iowait on the server.
I hope this helps someone.
I supported the new Linux Voice magazine with their Indegogo campaign and have just received the first digital issue. It is awesome and a great read. Given that the team is made up of mostly of ex-Linux Format employees, it shares some similarities. Well done Linux Voice!
I needed to connect to Oxford University via a VPN connection from my Ubuntu 13.10 laptop. They have some instructions by they are quite complicated and not very clear. Here is how I did it:
1 – Install a Cisco compatiable VPN Client
Oxford University uses the Cisco VPN. You can install this directly from the repositories.
sudo apt-get install network-manager-vpnc vpnc <code>network-manager-vpnc-gnome</code></pre> <pre>
2 – Update the VPN service
sudo nano /etc/dbus-1/system.d/nm-vpnc-service.conf
Add a new policy before the </busconfig>
<policy at_console="true">
<allow own="org.freedesktop.NetworkManager.vpnc"/>
<allow send_destination="org.freedesktop.NetworkManager.vpnc"/>
</policy>
You can save and close nano by ctrl-o (for saving files) and ctrl-x (for exiting).
3 – Get the settings…
Go to https://register.it.ox.ac.uk/self/index and follow these steps to get the settings. Note: you will need to login using your account details (these will be the same as your emails etc).
Login then select “Register for and download site-licensed software (Sophos, VPN)”
Select “VPNC Client for Linux/Unix”
Client the “vpnc configuration file”
… and up pops this window.
You will need all this information for the following steps.
4 – Configure the VPN Connection Locally
Click on the network icon at the top right of the screen. Select VPN connections -> Configure VPN…
In the Network Connections dialog box – click “Add”
Select “Cisco Compatitble VPN (vpnc)”. It you can’t see this option then you need to go back and install the VPNC client.
Fill in the fields as show below. You will need your University login and also the setting which we found before.
Then click “Save”. You can connect…
5 – Connect…
Click on the network icon and under “VPN Connections” – select the VPN connection that you have just created. The network icon will pulse and you should see this icon:
Let me know if this works or doesn’t work for you.
Happy VPN’ing.
Ansible is a great tool for configuring servers. I only recently discovered the Ansible diff argument which can be used to check what changes are going to be made for a file. If you use this with the –check flag you can see what changes will be applied. I find this especially useful when coming back to a project after a break.
ansible-playbook paybook.yml –check –diff –limit my.example.com
You can read the Ansible docs on this here:
Awesome.
If you have cut a pasted the demo.py script from Paramiko to test is working on your server then you might get this error:
import interactive ImportError: No module named interactive
There isn’t a python module called interactive – you need to download the interactive.py file which is included in the same folder as the demo application.
I just brought an Airplay device (an Audio Pro Allroom Air One) because I wanted to stream music from my iPhone and Synology NAS.
I followed the installation instructions and connected the Airplay device to the network. The device appeared as an option when playing music on the phone. However, the streaming started and after about 5 seconds the network crashed and music stopped playing.
I logged into the router and checked the signal strength:
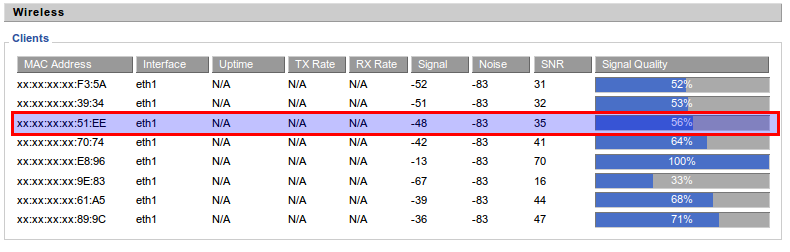
I knew it was a network crash because everything got kicked off. My Ubuntu laptop, the Airplay device and the phone all lost network connection.
The Solution
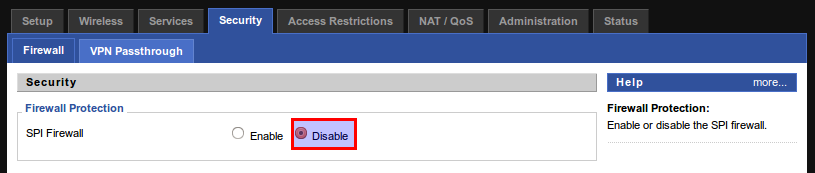
Step 1 – Disable the SPI Firewall.
On your router, go to Security -> Firewall. Disable the SPI Firewall, save changes and then apply them.
Step 2 – Change Network Security from WPA (TKIP) to WPA (AES)
Some of posts on Apples website suggest that changing from TKIP to AES will reduce the network crashes and this seems to be the case for me. To change this setting go to Wireless -> Security and select AES. Then save and apply changes. I found that I had to reconnect the AudioPro device to the network after making this change.
Step 3 – Enable JIFFS2
I have no idea why enabling jiffs2 would make a difference but it seems to. On the router, go to Administration -> Management and stroll near the bottom to enable jiffs.
…
Does this work for you?
If this works for you or if you find another way to stop Airplay freezing / killing your network then please let me know by leaving a comment.