I’ve been reading up a little about Google’s search rankings. Everyone says that Google rewards sites which are responsive. I thought that I would test this out by changing my site over to a responsive design. I’ll update the blog with the results.
How to clear apt-cacher cache – Ubuntu 14.04 – apt-cacher: Cache Full
We have a server running apt-cacher to help cache Ubuntu repositories. However, after about 2 years of usage the disk on the server has filled up. I discovered this after trying to update my Ubuntu desktop and got the following error:
503 apt-cacher: Cache Full
Here is how to clear the apt-cache cache.
sudo service apt-cacher stop
sudo rm -rf /var/cache/apt-cacher-ng/
sudo mkdir -p /var/cache/apt-cacher-ng/{headers,import,packages,private,temp}
sudo service apt-cacher start
Unable to locate package htpasswd – ubuntu
I just tried to install the htpasswd command and got the following error: Unable to locate package htpasswd. Turns out you need apache2-utils:
<code>sudo apt-get install apache2-utils</code>
How to redetect keyboard in Ubuntu
There isn’t a graphical tool to redetect keyboards in Ubuntu and you have use the command line:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure keyboard-configuration
How To Clear Your Apple Maps Search History in iOS 8
I wanted to clear my Apple Map search history because it was auto-completing the wrong things. However, it isn’t very obvious how to clear your Apple Map search history. Here is how I cleared it:
1 – Open the Apple Maps app.
2 – Click into the search bar at the top.
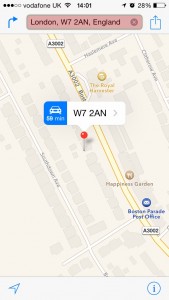
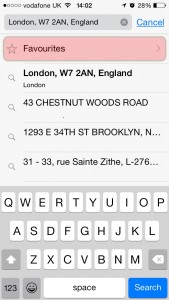
3 – Click on favourites
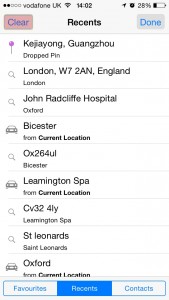
4 – Click the clear button.
Apple are generally great at usability. However, this simply doesn’t make sense to me and seems massively confusing. I wish that Apple would add a control clearing the search history from within the iPhone setting app. This would fit in with their general settings paradigm and is exactly how they do the clearing of Safari browser history.
Hope this helps someone.
PostgreSQL vs MS SQL…
I just read this awesome comparison of PostgreSQL vs MS SQL.
Great Image Viewer for Mac OS X … Lyn image browser
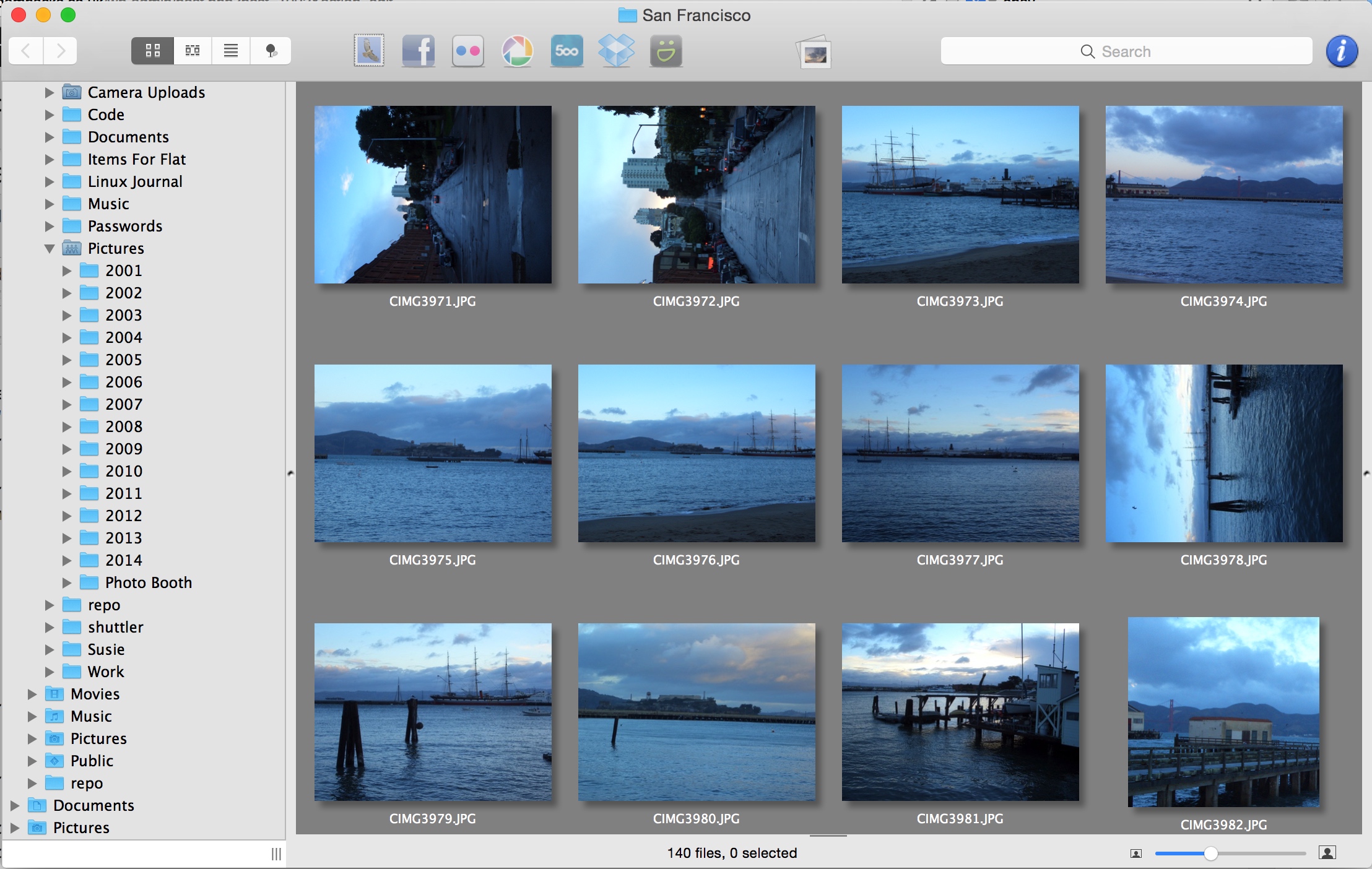
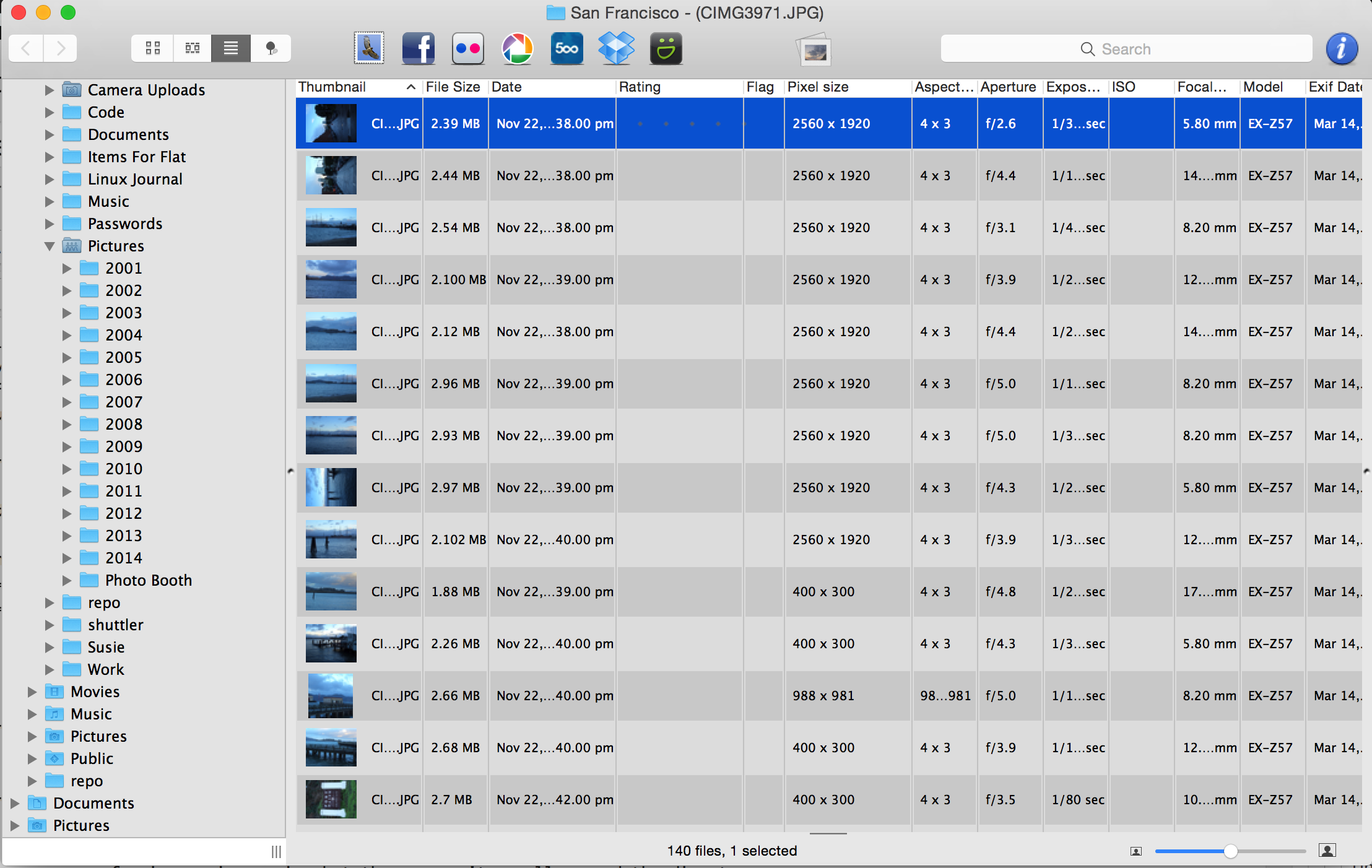
Apple Mac OS X is a brilliant OS but unfortunately it’s missing a good image viewer. In comparison, Windows has Preview and Ubuntu has the Gnome Image Viewer both of which are great. I did some research and the image browser i found was Lyn Image Browser. I like it so much… I thought I would put write a little review for it.
So why is it so good?
1 – Great Thumbnail Viewer
Lyn Image Browser has a great thumbnail viewer where the images are large enough to actually see them. You can browse through folders really quickly and easily.
You can also view all the image information:
2 – You can flick between images
This might not sounds like much of feature but frankly it is. Apple’s Preview is missing this key feature and is super annoying while both Windows preview and Gnome image viewer both have this feature.
Finally… its fast and lightweight
I hate slow applications and this one is very fast and lightweight and doesn’t hog the cpu.
So, if you are looking for a image viewer for Mac OSX then I can highly recommend Lyn Image Browser.
How give a user permission to run a specfic command as root Ubuntu
Sometimes it can be really useful to give a user privileges to run a specific command as root. For example – if you wanted to allow a user to restart a specific service or run a specific program as root without given them access to the whole server. You can configure this using visudo command as root. Note: you really must be root when you do this and not a sudo.
sudo su -
Then..
visudo
You can then modify the configuration file. There are specific sections in the config file which are show below. For example – I want to give a user called debug permission to run supervisorctl as root.
.... # User alias specification debug ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:/usr/bin/supervisorctl
Hope this is helpful.